Efficiency: Using resources in such a way to maximize the production of goods and services. Increases profits.
Under utilization: Opposite of efficiency. Using fewer resources than an economy is capable of using. Leads to decreased profits.
Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost: When resources are shifted from making one good or service to another, the cost of producing a second item increases.
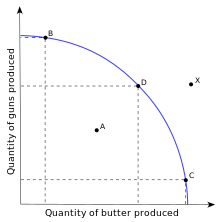
- Point D (on the curve)- Attainable & efficient
- Point A (inside the curve)- Attainable, but inefficient. Under utilization, unemployment or underemployment of resources.
- Point X (outside the curve)- Unattainable using current resources. Technology, Economic Growth.
Four Key Assumptions:
1. Only 2 goods can be produced
2. Full employment of resources
3. Fixed resources (factors of production)
4. Fixed Technology
Three types of movements that occur within the PPG:
 1. Inside the curve
1. Inside the curve 2. Along the PPC
2. Along the PPC 3. Shifts of the PPC
3. Shifts of the PPC
Two types of Efficiency
Productive Efficiency: - Products are being produced in the least costly way
- This is any point ON the production possibilities curve
Allocative Efficiency:
- The products being produced are the ones most desired by society
- This optimal point on the PPC depends on the desires of society
No comments:
Post a Comment